
Crystal Meth in Mumbai: India’s Strict Legal Stance and Trafficking Routes
Methamphetamine remains a drug with the potential to cause significant harm. For a major financial and transit hub like Mumbai, the threat from synthetic drugs is a primary concern for law enforcement. Mumbai is influenced by India’s **Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act**, which mandates severe, quantity-based penalties.
Regional Usage and Sourcing
Methamphetamine use is documented to be generally low in Europe, but is concentrated in certain Eastern and Central countries, as well as high-risk groups in major cities.
- Indian Context: India’s primary role in the global market has been as a **source for “controlled substances” (precursors)** used to manufacture the drug elsewhere. The domestic abuse trend is lower than in East Asia, but trafficking is a major concern.
- Sourcing: Methamphetamine is trafficked into India from Iran and Afghanistan, using established opiate routes. The drug trade is also influenced by production hubs in the Golden Triangle.
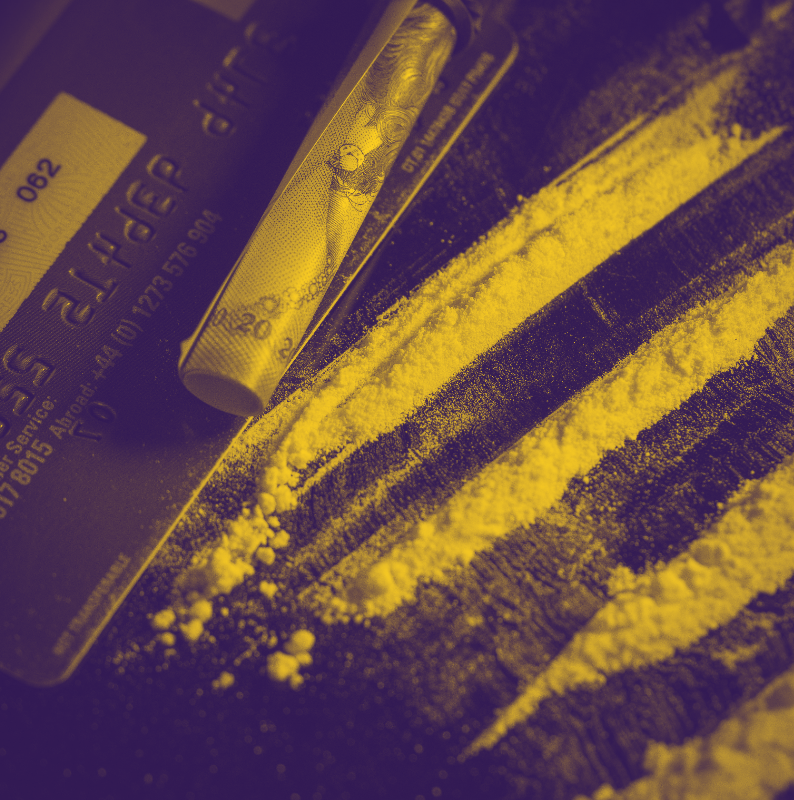
- Forms of Methamphetamine: Methamphetamine is available in powder form (often mixed with other ingredients like lactose) and highly pure crystalline form (“ice” or “crystal meth”).
Severe Health and Social Consequences
The harms associated with methamphetamine use are universal and pose a severe public health threat in any community, including Mumbai.
Physical Effects
- Cardiovascular Damage: Methamphetamine use immediately increases heart rate and blood pressure. Long-term abuse can lead to severe health problems like stroke, heart attack, and heart failure.
- Toxicity and Overdose: Use can cause fatal or non-fatal overdose (“overamping”), seizures, and a rapid, dangerous increase in body temperature (hyperthermia).
- “Meth Mouth”: Chronic use often results in severe tooth decay and loss. This is caused by a combination of drug-induced dry mouth (xerostomia), teeth grinding (bruxism), and poor hygiene.
- Infections: Injecting methamphetamine significantly increases the risk of acquiring and transmitting blood-borne viruses like **HIV and viral hepatitis**. It can also lead to bacterial infections, such as endocarditis (a heart infection).
Psychological Effects
- Psychosis and Paranoia: Long-term use is strongly linked to psychotic symptoms, including paranoia, visual and auditory hallucinations, and fixed, false delusions. A common delusion is the sensation of insects creeping under the skin (*formication*).
- Violent Behavior: Chronic users may exhibit aggressive and violent behavior due to agitation, paranoia, and severe mood swings.
- Cognitive Decline: Long-term abuse causes brain changes, resulting in deficits in memory, attention, problem-solving, and verbal learning.
Social and Community Impact
- Addiction: Methamphetamine has a high potential for abuse and dependence, leading to compulsive drug-seeking behavior.
- Community Harm: Methamphetamine use threatens whole communities, contributing to new waves of crime, unemployment, and child neglect or abuse.
- Economic Strain: The drug poses significant challenges to healthcare professionals and places a substantial burden on law enforcement and the legal system.
Legality and Penalties in India
India’s drug laws are consolidated under the **Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985**, which mandates severe, quantity-based penalties.
- Small Quantity (up to 2 grams): Imprisonment for up to 1 year and/or a fine up to Rs. 10,000.
- Commercial Quantity (50 grams or more): Rigorous imprisonment for **10 to 20 years** and a fine of Rs. 1 to 2 lakhs.
- Repeat Offenses: Repeat offenses for commercial quantities can attract enhanced punishments, including the **death penalty** in some cases.
- Treatment Immunity: Addicts who **volunteer for treatment** may receive immunity from prosecution.











No Comments